Friday 21 March 2025
A team of researchers has made a significant breakthrough in the field of robotics, developing an innovative approach for planning and optimizing the motion of tethered robots. These robots, which are essentially unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones attached to a cable, have numerous applications in various fields such as search and rescue, environmental monitoring, and construction.
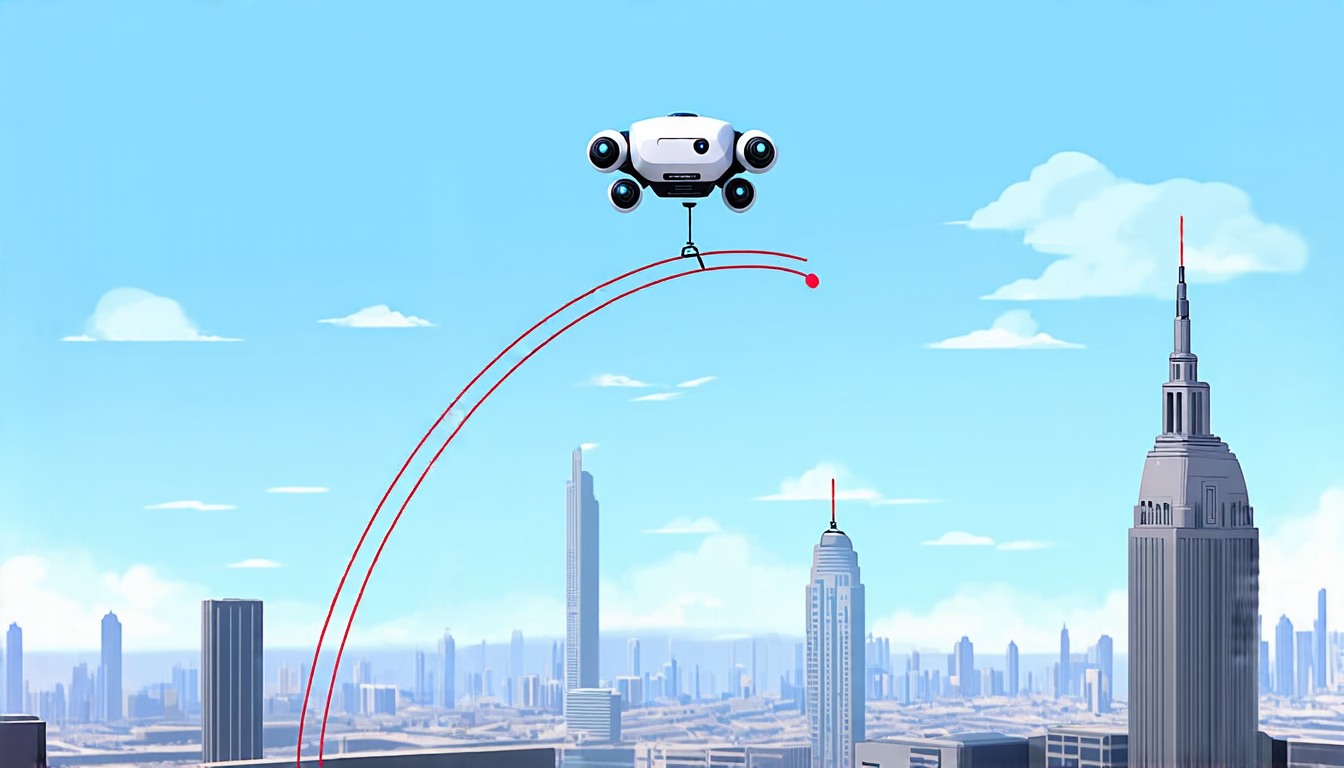
The traditional method of planning the motion of these robots involves solving complex mathematical equations, known as catenary curves, which describe the shape of the tether. However, this approach can be time-consuming and computationally intensive, making it challenging to use for real-time applications.
To address this issue, researchers have developed a new approach that approximates the catenary curve using a parabolic equation. This method is not only faster but also provides more accurate results, allowing for smoother and more efficient motion of the robot.
The team used a combination of mathematical modeling and computer simulations to test their approach. They created a virtual environment with various obstacles and scenarios, simulating real-world situations. The results showed that the parabolic approximation was able to generate smooth and collision-free trajectories for the tethered robots, outperforming traditional methods in terms of speed and accuracy.
One of the key advantages of this new approach is its ability to handle complex environments and scenarios. By using a parabolic equation, researchers can model the motion of the robot in three-dimensional space, taking into account factors such as obstacles, terrain, and wind resistance.
The potential applications of this technology are vast. For example, tethered robots could be used for search and rescue operations, allowing them to navigate through dense forests or urban areas with ease. They could also be used for environmental monitoring, tracking the movement of wildlife or monitoring air quality.
In addition, this approach could have significant implications for the construction industry. Tethered robots could be used for tasks such as inspecting bridges or buildings, or even performing maintenance and repair work in hard-to-reach areas.
The development of this new approach is a testament to the power of innovation and collaboration in the field of robotics. By combining mathematical modeling with computer simulations, researchers have been able to create a more efficient and effective way of planning and optimizing the motion of tethered robots.
As technology continues to evolve, it will be exciting to see how this breakthrough is applied in various fields and industries.
Cite this article: “Revolutionizing Tethered Robotics: A New Approach to Motion Planning”, The Science Archive, 2025.
Robotics, Tethered Robots, Uavs, Drones, Catenary Curves, Parabolic Equation, Mathematical Modeling, Computer Simulations, Search And Rescue, Environmental Monitoring