Friday 28 March 2025
A team of mathematicians has made a significant breakthrough in understanding the properties of graph theory, a branch of mathematics that studies connections between objects. The researchers have discovered counterexamples to Hedetniemi’s conjecture, a long-standing problem in graph theory that has puzzled experts for decades.
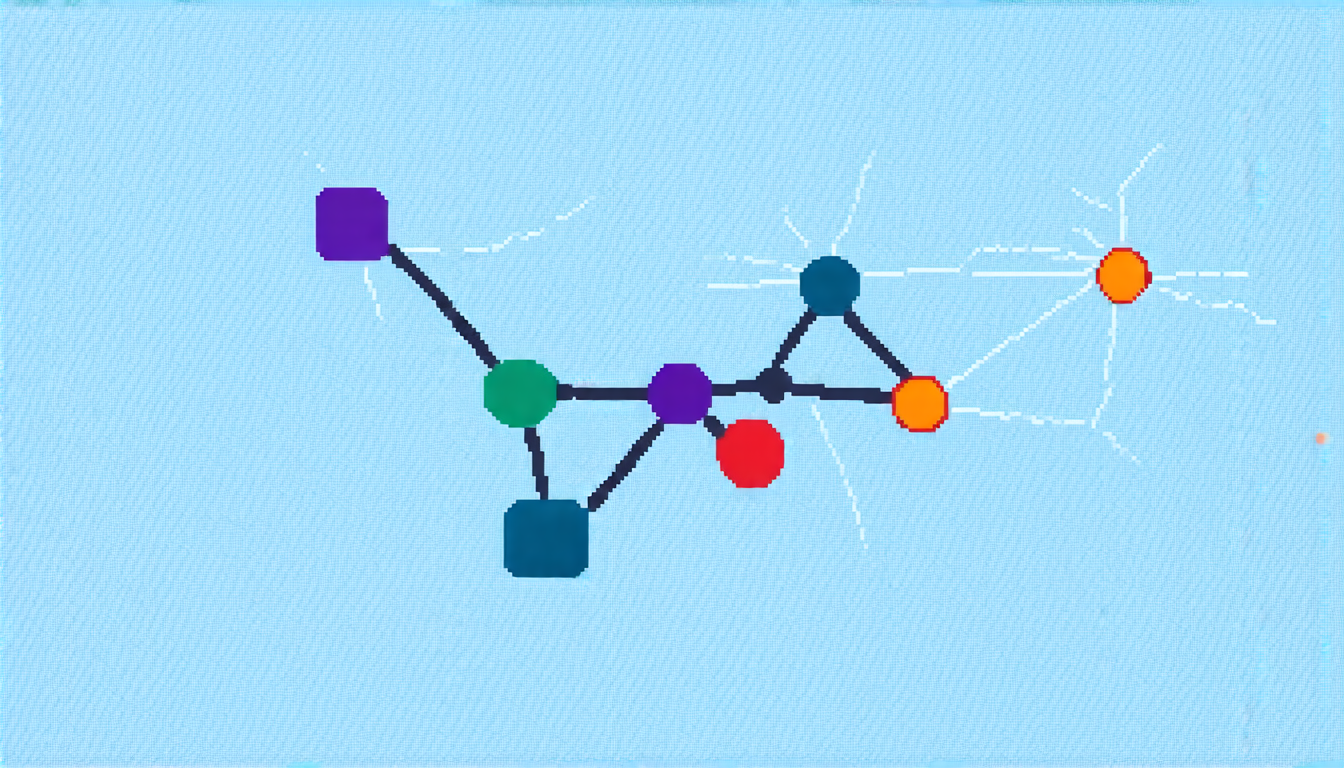
Graph theory is used to describe complex systems, such as social networks, transportation networks, and biological networks. It involves studying the relationships between individual components, known as nodes or vertices, which are connected by edges. The study of graph theory has far-reaching applications in computer science, physics, biology, and many other fields.
Hedetniemi’s conjecture, named after its proposer, Finnish mathematician S.A. Hedetniemi, states that the chromatic number of a graph product is equal to the minimum of the chromatic numbers of the two original graphs. The chromatic number of a graph is the smallest number of colors needed to color the nodes such that no two adjacent nodes have the same color.
The conjecture has been widely studied and debated in the mathematical community, with many attempts to prove or disprove it. However, until now, no one has been able to come up with a definitive answer.
The researchers used advanced mathematical techniques and computer simulations to create counterexamples to Hedetniemi’s conjecture. They discovered that there are certain types of graphs that do not satisfy the conjecture, meaning that the chromatic number of their product is different from the minimum of the chromatic numbers of the original graphs.
This breakthrough has significant implications for our understanding of graph theory and its applications in other fields. It shows that the field is more complex and nuanced than previously thought, with many unexpected behaviors and patterns emerging.
The discovery also opens up new avenues of research in graph theory, as mathematicians can now explore the properties of these counterexamples and develop new theories to explain their behavior. This could lead to further advances in fields such as computer science, physics, and biology, where graph theory is used to model complex systems.
In addition, the breakthrough has sparked renewed interest in Hedetniemi’s conjecture itself, with many experts now eager to revisit the problem and try to solve it once and for all. The discovery of counterexamples has shown that the conjecture is not as straightforward as previously thought, but rather requires a deeper understanding of graph theory and its underlying principles.
The study of graph theory is an active area of research, with new discoveries being made regularly.
Cite this article: “Graph Theory Breakthrough: Counterexamples to Hedetniemis Conjecture”, The Science Archive, 2025.
Graph Theory, Hedetniemi’S Conjecture, Counterexamples, Chromatic Number, Graph Product, Nodes, Vertices, Edges, Graph Decomposition, Mathematical Modeling
Reference: Xuding Zhu, “A survey on Hedetniemi’s conjecture” (2025).