Sunday 28 September 2025
The world of decision-making is often a complex and daunting task, especially when faced with multiple criteria and alternatives. In this chapter, researchers delve into the realm of aggregation-type multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods, providing insight into eight distinct techniques designed to simplify this process.
At its core, MCDM involves evaluating alternatives based on various criteria, ultimately ranking them in order of preference. Aggregation-type methods take a step further by combining these values and weights to produce a single performance score for each alternative. This simplifies the decision-making process, allowing for quicker identification of the most suitable option.
The eight methods explored in this chapter are: Simple Additive Weighting (SAW), Multiplicative Exponent Weighting (MEW), Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Analytic Network Process (ANP), Complex Proportional Assessment (COPRAS), Multi-Objective Optimization on the basis of Ratio Analysis (MOORA), Faire Un Choix Adéquat (FUCA), and Weighted Aggregated Sum Product Assessment (WASPAS).
Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, with some being better suited to specific decision-making scenarios. For instance, SAW is a straightforward technique that assigns weights to criteria based on importance, while MEW uses an exponential function to combine values and weights. AHP and ANP, on the other hand, involve pairwise comparisons to determine relative priorities.
COPRAS, MOORA, and FUCA employ different approaches to aggregating criteria values, with COPRAS using a complex proportional assessment, MOORA optimizing based on ratio analysis, and FUCA employing a unique formula. WASPAS, meanwhile, combines weighted aggregated sums with product assessments.
The chapter presents each method in detail, providing step-by-step instructions and numerical examples. This allows readers to easily understand the principles behind each technique and how they can be applied to real-world scenarios.
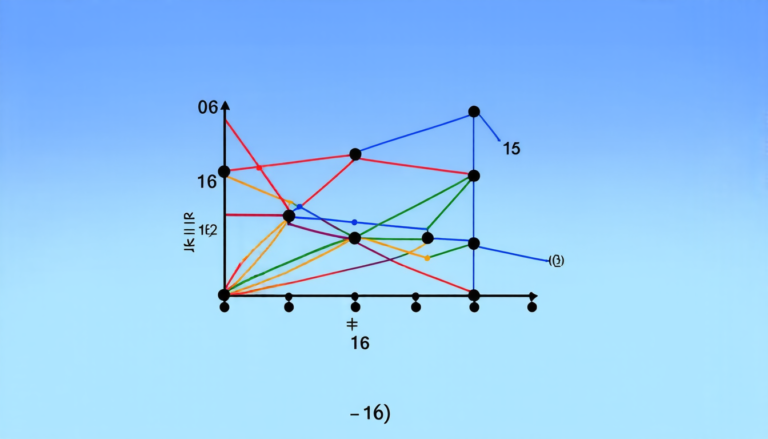
One of the key findings is that different methods can lead to varying rankings of alternatives. For instance, SAW, MEW, COPRAS, MOORA, FUCA, and WASPAS all identify A3 as the top-ranked alternative in a given example, while AHP ranks A1 highest. This highlights the importance of considering multiple perspectives when making decisions.
The chapter concludes by emphasizing the role of MCDM methods in facilitating effective decision-making.
Cite this article: “Simplifying Decision-Making: An Exploration of Aggregation-Type Multi-Criteria Methods”, The Science Archive, 2025.
Multi-Criteria Decision-Making, Aggregation-Type Methods, Decision Analysis, Alternative Ranking, Weighting Systems, Evaluation Criteria, Optimization Techniques, Performance Scores, Analytics, Choice Modeling